Blockchain technology

Blockchain technology ko samajhne aur uspe kaam karne ke liye aapko niche diye gaye areas me knowledge honi chahiye:
1. Programming Languages
Blockchain development ke liye programming aana zaroori hai. Kuch important languages:
✅ Solidity – Ethereum Smart Contracts ke liye
✅ Rust – Solana, Near Protocol ke liye
✅ Go (Golang) – Hyperledger Fabric, Cosmos SDK ke liye
✅ JavaScript & TypeScript – Web3.js aur DApps development ke liye
✅ Python – Smart contract scripting aur blockchain automation ke liye
2. Data Structures & Algorithms
Blockchain decentralized aur distributed hoti hai, isliye aapko data structures aur algorithms samajhne padenge:
✅ Linked Lists – Blocks ko chain karne ke liye
✅ Merkle Tree – Transactions verification ke liye
✅ Hashing (SHA-256, Keccak-256) – Data integrity maintain karne ke liye
✅ Graphs & DAGs (Directed Acyclic Graphs) – Blockchain alternative structures (IOTA, Hedera Hashgraph)
3. Cryptography (Blockchain Security)
Blockchain me security aur encryption bahut important hai. Aapko samajhna hoga:
✅ Public-Key Cryptography (PKC) – Wallets aur Transactions ke liye (RSA, ECDSA)
✅ Hashing Algorithms – Data integrity ke liye (SHA-256, Keccak-256, Blake2b)
✅ Digital Signatures – Authentication aur security ke liye
✅ Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKP) – Privacy-focused transactions (zk-SNARKs, zk-STARKs)
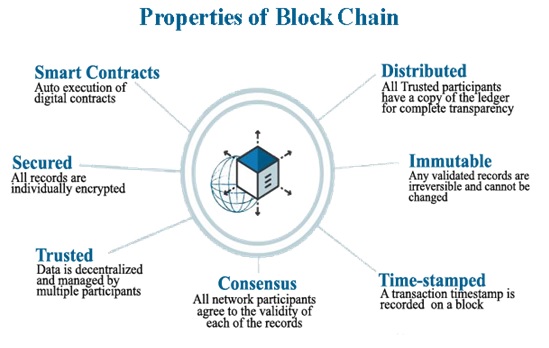
4. Blockchain Fundamentals
Agar aap blockchain me kaam karna chahte hain, to sabse pehle iske basic concepts samajhne honge:
✅ Decentralization – Koi single authority nahi hoti
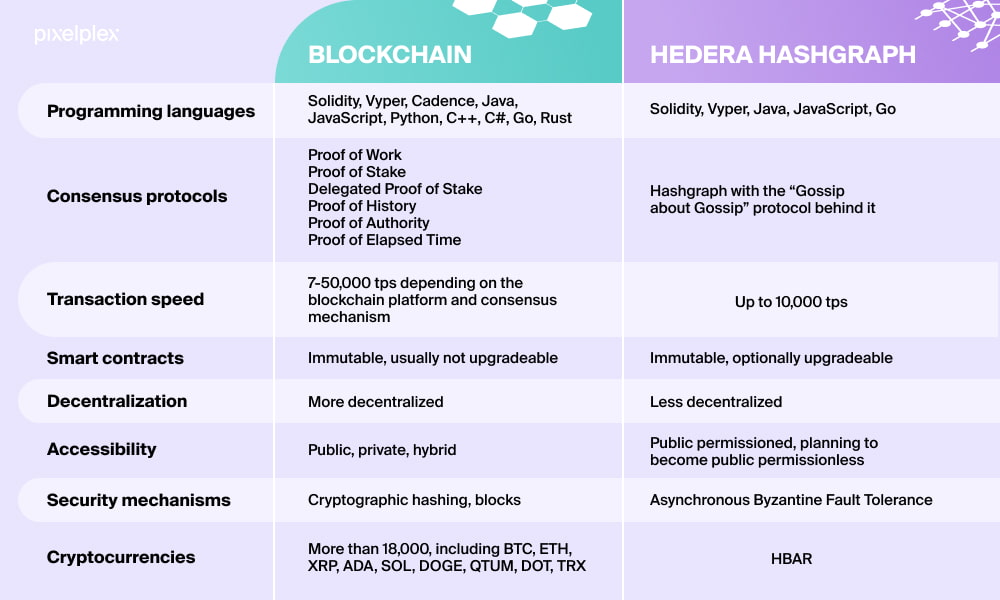
✅ Consensus Mechanisms – PoW, PoS, DPoS, PoH
✅ Mining & Validation – Blocks validate kaise hote hain
✅ Transactions & Gas Fees – Crypto transactions aur fees kaise kaam karti hai
✅ Layer 1 vs Layer 2 Solutions – Ethereum, Solana vs Polygon, Lightning Network
5. Smart Contract Development
Smart contracts blockchain ke automated programs hote hain. Aapko inme expertise honi chahiye:
✅ Solidity (Ethereum Smart Contracts)
✅ Rust (Solana & Near Protocol)
✅ Web3.js & Ethers.js (DApps Development)
✅ Security Vulnerabilities (Reentrancy, Integer Overflow, Front-running, etc.)
6. Blockchain Platforms & Ecosystem
Different blockchain platforms aur unke use-cases samajhna zaroori hai:
✅ Bitcoin (BTC) – Digital gold, Proof-of-Work
✅ Ethereum (ETH) – Smart contracts aur DApps
✅ Binance Smart Chain (BSC) – Fast & low-fee transactions
✅ Solana (SOL) – High-speed transactions
✅ Polkadot & Cosmos – Interoperability aur multi-chain solutions
7. Decentralized Applications (DApps) & Web3
Blockchain se judi applications aur frameworks me kaam karna aana chahiye:
✅ IPFS (InterPlanetary File System) – Decentralized Storage
✅ Web3.js & Ethers.js – Blockchain interaction
✅ NFT Development (ERC-721, ERC-1155) – Digital assets
✅ DeFi Protocols (Aave, Uniswap, Compound)
8. Consensus Mechanisms
Different blockchains ke alag consensus algorithms hote hain. Aapko samajhna hoga:
✅ Proof-of-Work (PoW) - Bitcoin, Ethereum (Old)
✅ Proof-of-Stake (PoS) - Ethereum 2.0, Cardano
✅ Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) - EOS, TRON
✅ Proof-of-History (PoH) - Solana
9. Cybersecurity & Blockchain Security
Blockchain me security vulnerabilities aur attacks se bachna bhi zaroori hai:
✅ 51% Attacks – Bitcoin aur PoW blockchains me risk
✅ Reentrancy Attacks – Smart contracts ke flaws
✅ Front-running – Miner Extractable Value (MEV) attacks
✅ Phishing & Social Engineering – Crypto wallet hacks
10. Regulations & Legal Frameworks
Agar blockchain aur crypto industry me kaam karna chahte hain, to legal aspects bhi samajhne honge:
✅ KYC/AML Compliance – Crypto exchanges ke rules
✅ SEC & CFTC Regulations – Crypto assets ka legal status
✅ CBDCs (Central Bank Digital Currencies) – Government-backed digital currencies
11. Blockchain Development Tools & Frameworks
Development ke liye aapko tools aur frameworks ka knowledge hona zaroori hai:
✅ Truffle & Hardhat – Smart contract development
✅ Ganache – Local Ethereum blockchain for testing
✅ Remix IDE – Solidity development
✅ Infura & Alchemy – Blockchain node access
✅ Metamask & WalletConnect – Wallet integrations
12. Career Opportunities in Blockchain
Agar aap blockchain seekh rahe hain, to is field me kaun kaun se career options available hain:
✅ Blockchain Developer (Smart Contracts, DApps)
✅ DeFi Developer (Decentralized Finance)
✅ NFT Developer (Gaming, Art, Metaverse)
✅ Blockchain Security Analyst (Cybersecurity, Audits)
✅ Blockchain Consultant (Business Strategy, Enterprise Solutions)
✅ Crypto Trader/Analyst (Trading, Investment)





Comments
Post a Comment