Cloud engineers are IT professionals
- Compute services
- Storage services
- Database services
- Networks or VPN
- Load balancing and scaling
- Cloud monitoring
- Application migration
- Computer science
- Information systems and technology
- Software engineering
- DevOps, a popular framework that combines development and operations
- Hands-on understanding of DevOps practices
- Expertise in programming languages, such as Java, Python, and Ruby
- Familiarity with cloud services like Azure, AWS, GCP, Oracle, and Hadoop
- IT fundamentals and applications.
- Network and security.
- Web development.
- Scripting and automation.
- Cloud computing and architecture.
- Data management.
- Systems administration.
- Security testing.
Cloud Computing Tutorial for Beginners
Cloud Computing Tutorial: Table of Contents
Lesson 1: What is Cloud Computing and Who Utilizes Cloud Services?
Cloud computing is a delivery model for online services that enable customers to access applications and data over the internet, rather than through local or corporate servers. Cloud services are often used by businesses who need to offload certain tasks from their main systems, or who want to use remote resources for faster application deployment. Examples of popular cloud services include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Microsoft Azure, IBM Bluemix, and Oracle Cloud Service.
Lesson 2: Benefits, Features, and More of Cloud Computing Architecture
Cloud computing is a rapidly growing trend in business today. This allows users to use resources from remote data centers instead of having them located on their premises. It also allows businesses to access software and data from remote servers instead of installing it on their internal systems. This provides many benefits, including increased efficiency and cost savings. There are two main types of cloud architectures: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS).
Lesson 3: VMware Workstation: Everything You Need to Know
VMware Workstation is a powerful virtual machine software that allows users to run multiple operating systems and applications on one computer. It's perfect for use in corporate environments, where different departments need their operating system or application suite. Plus, because it integrates with other VMware products (such as vSphere), it provides comprehensive management of your computing resources.
Lesson 4: Which Cloud Platform Should You Pick in 2022 Between AWS and Azure?
AWS and Azure are two of the most popular cloud platforms on the market today. Which one should you choose in 2022? When it comes to which platform is better, there are a few things to consider. These include customer base, cost-effective architecture, scalability, security, and availability.
Lesson 5: Google Cloud vs. AWS: Choosing the Right Platform
When it comes to cloud computing, there are a few different options available. Google Cloud and AWS (Amazon Web Services) are two of the most popular platforms, but which one is right for your business?
In this article, we compare Google Cloud and AWS, two of the most popular cloud platforms.
Lesson 6: How to become a cloud engineer?
Becoming a cloud engineer is one of the most in-demand jobs in today's tech industry. As the world becomes increasingly digital and mobile, there is an increasing need for engineers who can create and maintain reliable computing systems that meet the high demands of tomorrow's businesses.Check out Simplilearn Programs PGP Cloud Computing and Cloud Architect.
Find our Cloud Architect Online Bootcamp in top cities:
| Name | Date | Place | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud Architect | Class starts on 16th Mar 2024, Weekend batch | Your City | View Details |
| Cloud Architect Course in Hyderabad | Class starts on 23rd Mar 2024, Weekend batch | Hyderabad | View Details |
| Cloud Architect Course in Pune | Class starts on 25th Mar 2024, Weekdays batch | Pune | View Details |
What is Cloud Computing and Who Uses Cloud Services?
Cloud Computing is a network of remote servers hosted on the internet for storing and retrieving data. The cloud provides a number of IT services such as servers, databases, software, virtual storage, and networking, among others. In layman’s terms, Cloud Computing is defined as a virtual platform that allows you to store and access your data over the internet without any limitations.
Companies that offer all the services mentioned above are called cloud providers. They provide you with the ability to store and retrieve data and run applications, managing them through configuration portals. Two of the best cloud providers available today are Amazon Web Services and Microsoft Azure.
Now that you know what is cloud computing, let’s see what are the benefits of cloud computing.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
Cloud platforms offer some significant benefits today, which are driving businesses to adopt Cloud Computing. Those major benefits include:
- Speed
- Cost
- Scalability
- Accessibility
- Better Security
1. Speed
If you want an IT resource or service from the cloud, it is available almost instantaneously, and ready for production virtually at the same time. This means that the product, service, and the go-live date hit the market almost immediately, a considerable advantage over using a legacy environment. This has helped many businesses’ services generate revenue much sooner after they go live.
2. Cost
Planning and buying the right kind of hardware has always been a challenge in the traditional legacy environment. If you purchase hardware that doesn’t fit your needs, then chances are you might need to live with that purchase indefinitely. However, this is not an issue with the cloud, since you do not need to buy any hardware. Instead, you pay to use the host’s hardware, and once it does not fit your needs, you can release it and can replace it with a better configuration. In that way, you save a lot of money since you only pay for the time you use.
3. Scalability
In a legacy environment, forecasting demands is a full-time job, but with cloud services, you can easily set up an automated monitoring tool to do the job for you. That information will let you accurately upscale or downscale the rate of work you do depend on the needs.
4. Accessibility
Cloud Computing allows you to access resources, data, services, and applications from anywhere you want, as long as you are connected to the internet. If you are not connected to the internet, some tools and techniques will allow you to access the cloud whenever needed.
5. Better Security
Ensuring that your data is stored in a secure, durable place is a priority for all businesses. The cloud provides highly secure storage for customers’ data, yet letting it be accessed anytime and anyplace that it’s required. Also, all data stored in the cloud is encrypted and secured so that it cannot be tampered with.
Alankar Dwivedi regained his confidence after completing the Post Graduate Program in Cloud Computing and started his technical consulting firm. Read his fabulous success story in our Simplilearn Cloud Architect Course Review here.
Let’s now look at the types of cloud computing in this what is cloud computing Bootcamp article.
Types of Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing is multiplying, resulting in it being classified into several different categories. However, out of various categories, there are six that stand out. These six categories are further divided into two parts: the category of cloud-based deployment and the category of cloud-based services.
Cloud Computing is divided into three categories based on deployment, including:
- Public cloud
- Private cloud
- Hybrid cloud
The remaining three categories are divided based on the services they offer, including:
Now that you have a better idea of what the cloud categories are let’s learn more about them in-depth.
Cloud Categories Based on Deployment Models
1. Public Cloud
In a public cloud, everything is stored and accessed through the internet. This deployment system allows anyone with proper permissions to access some of the applications and resources. The most exciting part about the public cloud is that you own none of the components present in it, be it the hardware, software, or application. All the components here are managed by the provider. Amazon Web Services and Microsoft Azure are two prominent examples of the public cloud.
2. Private Cloud
A private cloud is used exclusively in organizations, which they can run locally or choose to outsource it to other cloud services providers. This infrastructure runs strictly on a private network, which means that people present in the network can only access it. VMware cloud and some of the AWS products are some of the examples of a private cloud.
3. Hybrid cloud
It is probably the fascinating form of Cloud Computing that contains the functionality of both public and private clouds. Organizations using the hybrid cloud can choose to keep some of their data locally and some on the cloud. NASA is the best-known example of an organization that uses a hybrid cloud. It uses a private cloud to store sensitive data and uses the public cloud to save and share data that can be viewed by the public worldwide.
Cloud Categories Based on Service Models
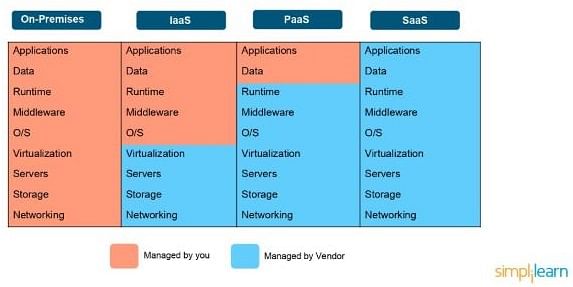
1. IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
This category consists of IT infrastructure that you can rent from a cloud provider on a pay-as-you-go basis, including servers, networks, and others. The best part about this service is that you have access to the services you provisioned, and some grant you root-level access as well. EC2, or the AWS Elastic Compute Cloud, is an excellent example of IaaS.
2. PaaS (Platform as a Service)
In this model, you are supplied with a pre-built platform from the cloud providers, where you can deploy your codes and applications. You only need to manage the codes and the applications, not the infrastructure. AWS Elastic Beanstalk is an example of a PaaS cloud.
3. SaaS (Software as a Service)
Here, the cloud providers offer you the end product, which could be an application or software that you can buy directly on a subscription. As a part of this service, the client maintains control of the software environment but does not maintain any equipment. There are some products of AWS and Microsoft Azure that provide SaaS.
Now, as you know what is cloud computing, its benefits, and the cloud categories, let's have a look at the difference between Iaas, Paas, and SaaS.
Difference Between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
Here’s a chart that clearly shows you the difference between the cloud categories based on their services:
Let’s now look at who uses the cloud in this what is cloud computing article.
Who Uses Cloud Services?
There are several well-known organizations across the world that have already migrated to the cloud environment. Some of the examples include:
Pinterest
Uses the AWS cloud environment to manage multiple petabytes of data that are generated by its users every day.Spotify
Uses the AWS cloud environment to store its vast repository of songs.Netflix
One of the largest video streaming services, it uses AWS to allow users to stream shows from anywhere in the world.Expedia
Uses AWS cloud services to accommodate a highly scalable infrastructure.
Conclusion
With 83% of the total enterprise workload expected to be on the cloud by the year 2020 and 75% of all the non-cloud apps expected to move to the cloud, today’s computing landscape is witnessing a great transition. Most organizations and businesses are finding ways to migrate to the cloud for better storage opportunities, scalability, and various other services that the cloud offers. Even with all of this, the cloud journey for many organizations has just begun, and the future with cloud services looks very bright with endless opportunities to explore.
Embrace the growing need for Cloud Computing experts with our Cloud Computing Courses that teaches you what is cloud computing and all its nuances which consist of the AWS Solutions Architect Training, Certified Azure Developer Associate Course, and more, that are designed to accelerate your career in this exciting field.
What Are VMware and Virtualization?
- In simple terms, VMware builds virtualization software
- Virtualization software generates an abstraction layer over computer hardware
- This layer allows the hardware elements (like RAM, memory, storage, and more) to be categorized into multiple virtual machines
What is a Hypervisor?
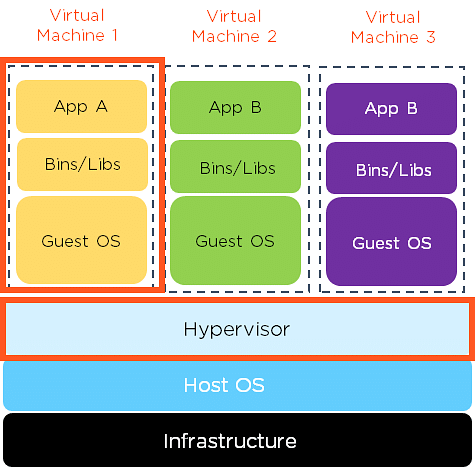
- A virtual machine (VM) is an isolated computing environment or software that allows users to operate applications on an operating system via a physical machine
- Each application consists of separate libraries and a guest OS. As shown in the diagram above, the hypervisor comes beneath the virtual machine. So what is a Hypervisor?
- A Hypervisor is a firmware that builds and runs virtual machines
- Every hypervisor consists of two types:
- Type 1 hypervisors are HyperKit for MacOS, Hyper-V for Windows, and KVM for Linux
- Type 2 hypervisors are VirtualBox and VMWare
Use of Hypervisor:
Consider an example where you want to run 2 apps on your server in total isolation. This process would require 2 guest operating systems, which are controlled by a hypervisor.
Benefits of Hypervisor
Some of the most common benefits of the hypervisor are:
- Cost-efficiency
- Flexibility
- Portability
- Easy setup and maintenance
- Better resource allocation
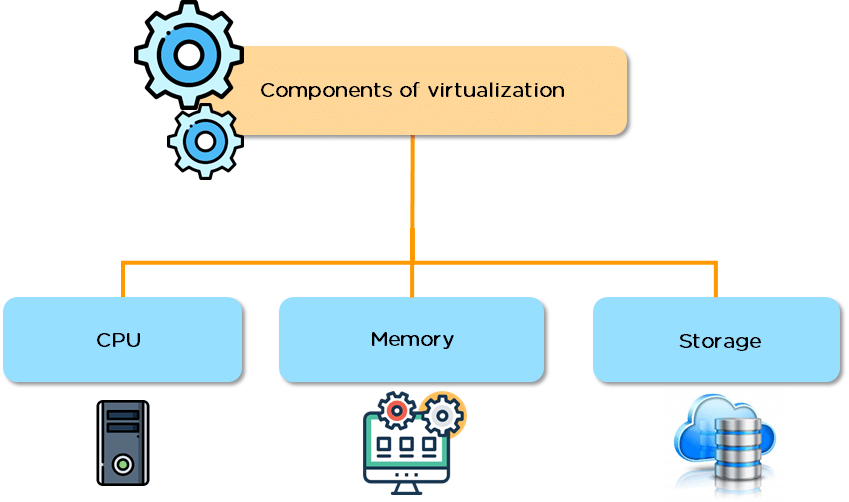
How Components of Virtualization Work?
CPU
- When a developer installs a hypervisor in a machine, you abstract each CPU into the virtual CPU
- This allows multiple VMs to share a processor core
- In simple words, hypervisor typically assigns one workload per CPU
Memory
- In simple words, virtual memory is the RAM of a computer machine
- The virtual machine settings show how much of the host's memory is allocated to the virtual machine
- The memory size shows how much memory is available to the application available in the virtual machine
- With this resource, a developer can add and modify the virtual machine capacity
Storage
- In virtualization, the storage component is the data cluster from multiple network storage devices
- It manages the storage components from a central console
- You can assign required storage to virtual machines manually
- The extensions on the end of a file are:
- VDI
- VHDX
- VMDK
- HDD
Note: However, different hypervisors like to use different file types.
Demo - Installing, Creating, and Duplicating VMware Workstation
VMware provides the facility to run on multiple workstations. It encourages an individual to create, test, and run software on the same system with minimum configuration requirements.
In the demo, we will look at the following:
- Installing VMware Workstation Player
- Creating a VM with VMware Workstation
- Duplicating a VM Using VMware Workstation
Installing VMware Workstation Player
Link to download VMware player: https://www.vmware.com/products/player/playerpro-evaluation.html
Step 1 − Go to the website and select "Download Now"
Step 2 − Once you download the file → double click on "Next"
Step 3 − Then, a window will pop up for setup; read the following instructions → Click "Next"
Step 4 − To proceed further, tick the box "I accept the terms in the license agreement" → Click on "Next"
Step 5 − Again, select the "Next" button
Step 6 − Click on "Finish"
Congratulations, you have successfully installed the player.
Creating a VM With VMware Workstation
To create a VM, follow the steps given below.
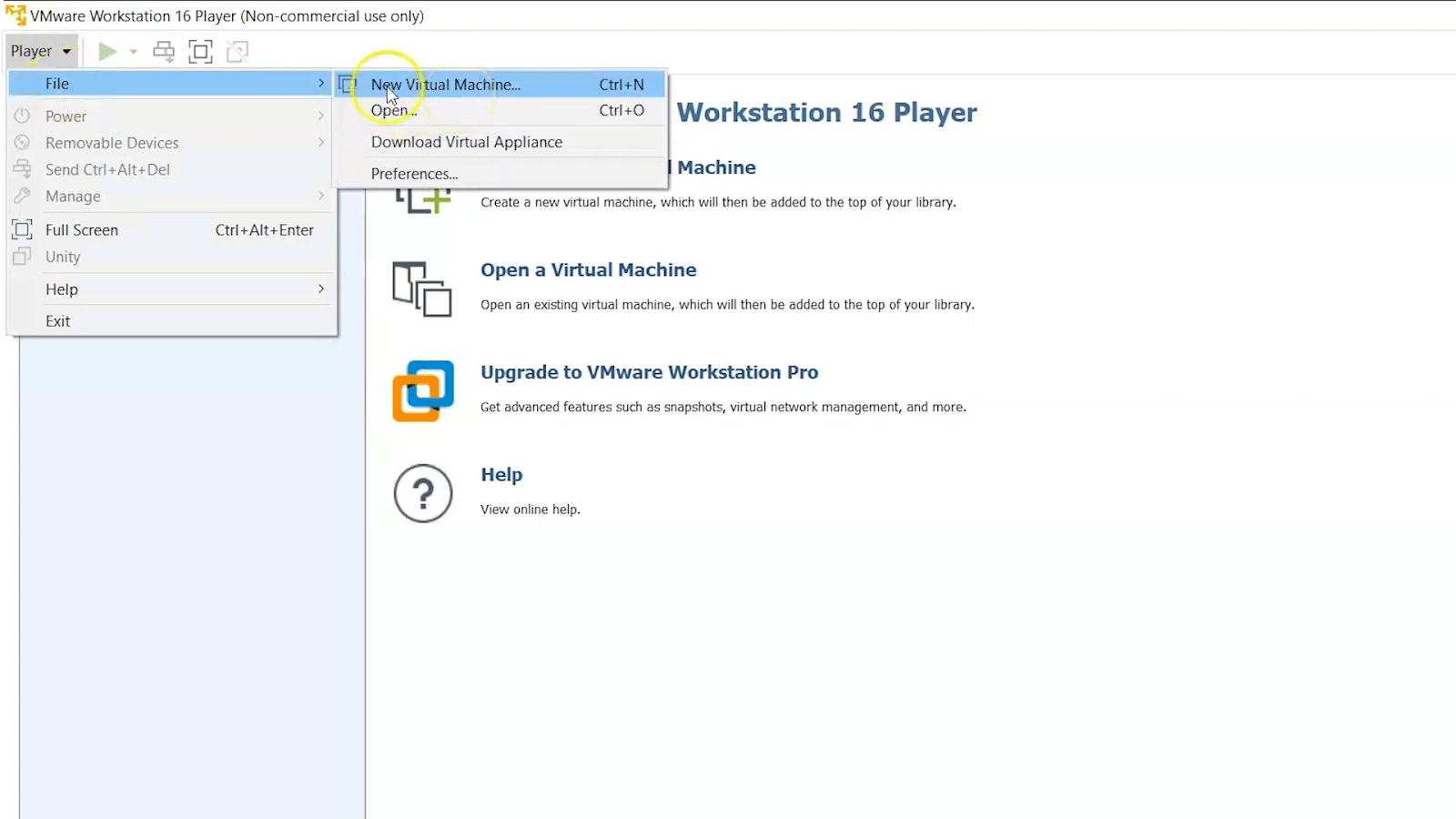
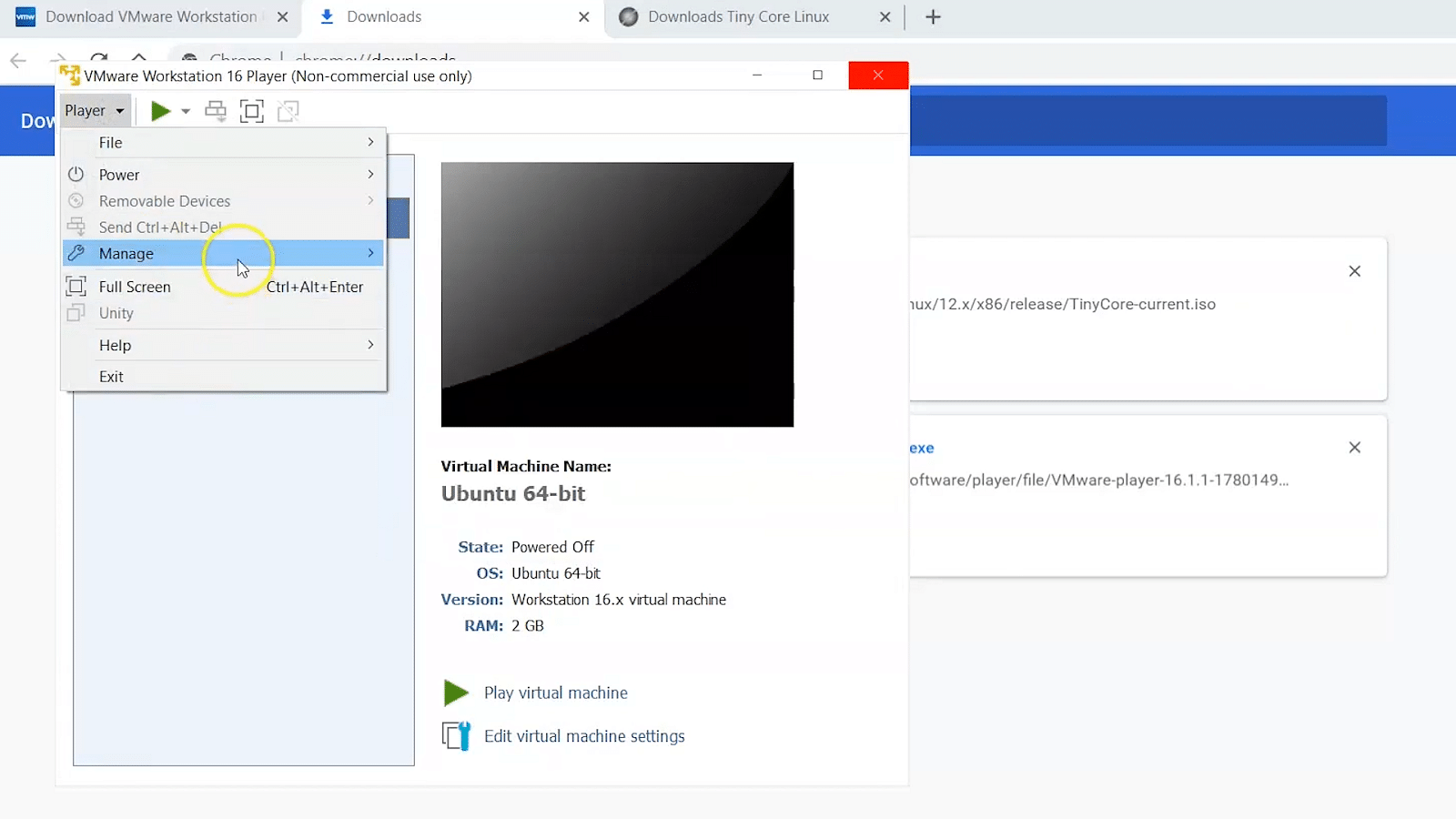
Step 1 − First, click on "Player" → File → New Virtual Machine
Step 2 − A table will pop up requesting you to find a "Boot disk," "Boot Image," or to install OS at a later stage.
In this case, you should select the second option and proceed by selecting the "Browse" option. Later, you should choose the ISO image that you want to install. Once the process is complete, click on "Next".
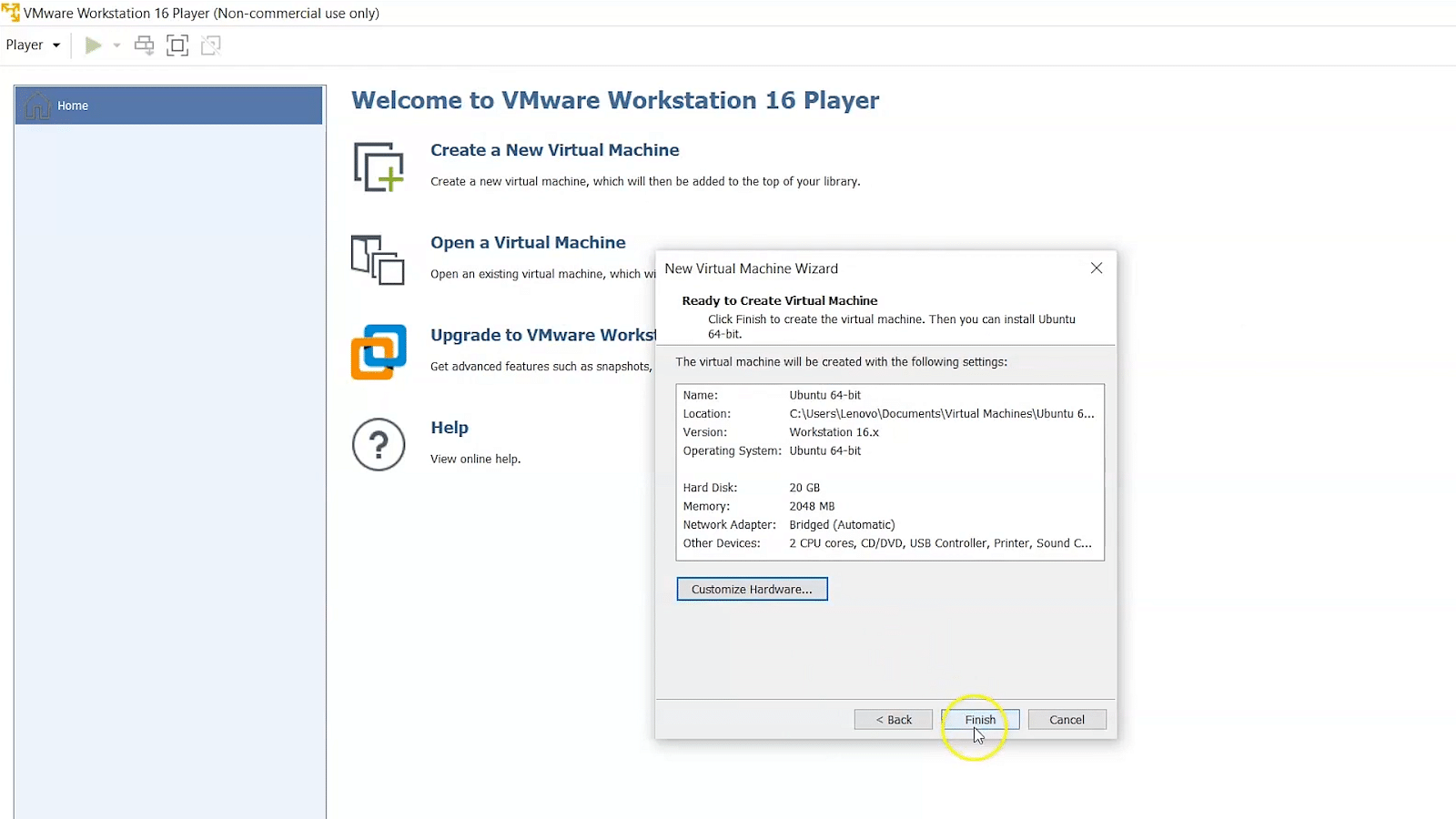
Step 3 − In this case, proceed with the Windows Server 2012 installation. Suppose you want to activate the noncommercial version of windows, click on "Next"
Step 4 − Now, enter the required size for your virtual hard disk within the "Maximum size disk" dialog box. Then click on "Next"
Step 5 − Select the "Finish" option
Network Setting With VMware Workstation
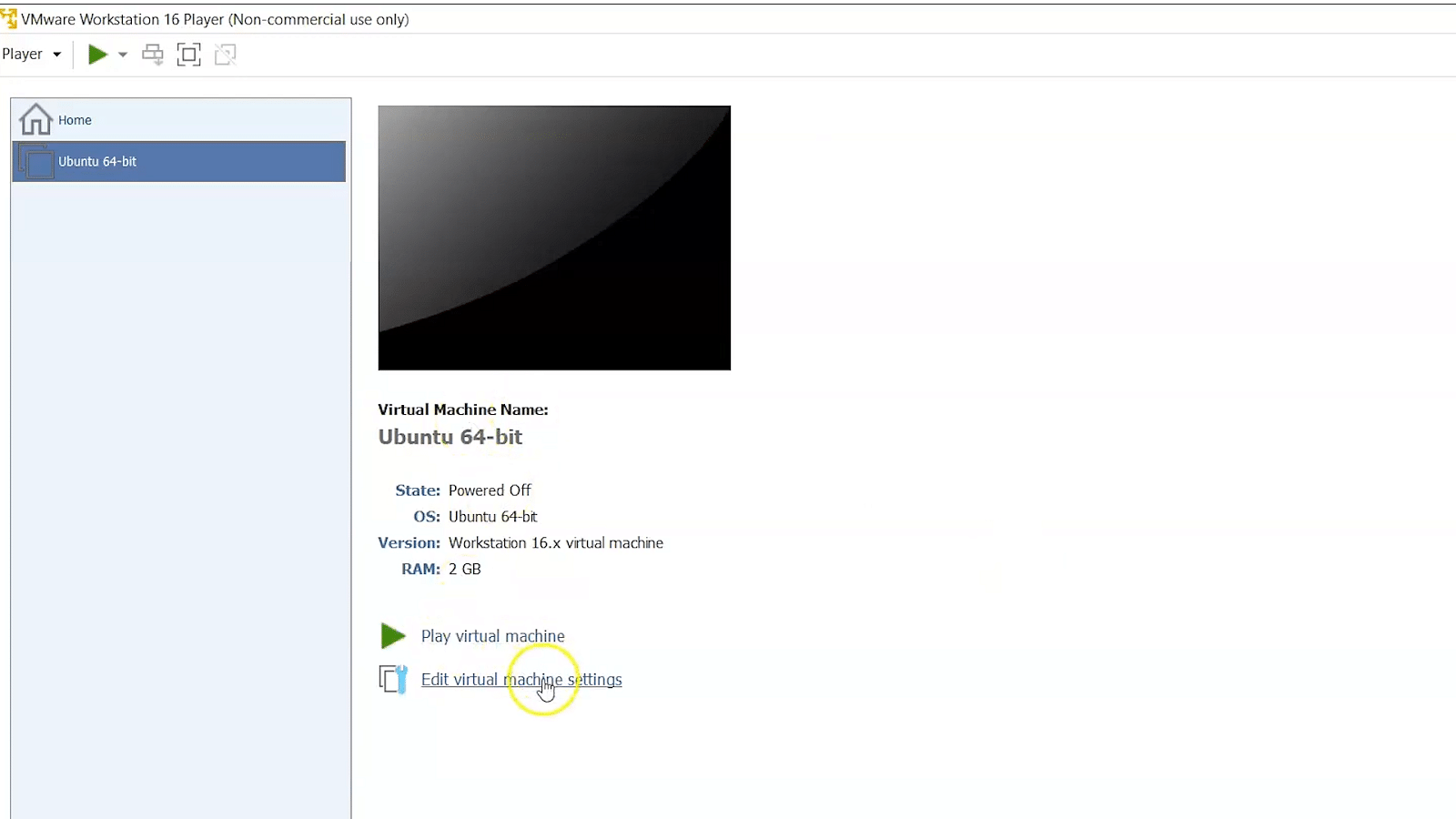
Step 1 - To set up the networking modes of a virtual machine in a VMware, click on the "Edit virtual machine settings".
Step 2 - Once you select edit, it will display a window on the left-hand-side panel. In that, select the "Network Adaptor" option.
Step 3 - After this, if you want to scale down the bandwidth usage of a virtual machine, click on the "Advanced" option and set the incoming and outgoing bandwidths accordingly.
Duplicating a VM Using VMware Workstation
To create duplicates of VM machines, you should use VMware Commercial Version.
Start with the process by following the instructions below.
Step 1 − First, open the VMware managing console and right-click on a VM you want to duplicate. Click on "Manage -> Clone," it will direct you to a new window
Step 2 − Now, click on “Next -> create full clone -> Next”
Step 3 − Enter a name for the clone and select "Finish"
Note: Once the cloning process is complete, it creates a duplicate VM.
AWS vs Azure: Which Cloud Platform Should You Choose in 2024?
Cloud service providers like Microsoft Azure and AWS have more in common with superheroes than one might think. Cloud storage companies touch the lives of millions; often making the world a better place.
In the battle of AWS vs Azure, Azure and AWS are superheroes in their own rights—but, who is on the top of the cloud?
A superficial glance might lead you to believe that AWS has an unprecedented edge over Azure, but a deeper look will prove the decision isn’t that easy. To determine the best cloud service provider, one needs to take multiple factors into consideration, such as cloud storage pricing, data transfer loss rate, and rates of data availability, among others.
From elementary schools to NASA, clouds have touched every sphere of our lives. Who said superheroes are just found in comic books?
Let us begin with to know the winner of the AWS vs Azure battle.
What is AWS?
All data scientists are assumed to be familiar with Amazon Web Services (AWS). Its original purpose after its 2006 introduction was to manage Amazon's e-commerce activities. Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a cloud computing platform created and operated by Amazon. Amazon Web Services has a wide range of global cloud-based products for business use. The pay-as-you-go pricing model is used for storage, databases, analytics, networking, mobile, development platforms, and enterprise applications.
What is Azure?
On February 1, 2010, Azure was officially released as Windows Azure. However, by the end of March 2014, it was officially known as Microsoft Azure. Microsoft Azure is a cloud computing service that allows users to create, modify, test, deploy, and maintain applications. It also provides free access for the first 12 months. It makes our work easier by giving us virtual machines, fast ways to process data, tools for analysis and monitoring, and so on. Azure's pricing is also easy to understand and less expensive. People often say, "Pay as you go," which means that you only pay for what you use.
AWS vs Azure: The Origins of AWS
In the early 2000s, Amazon was forced to re-examine its development platforms as they catered to their third-party clients. Over the years, they had created a jumbled mess of IT infrastructure where multiple teams worked in silos—often performing the same tasks—with no thought given to efficiency. In an effort to improvise, Amazon’s software team detangled the mess that was their infrastructure and replaced it with well-documented APIs. All was quiet until 2003 when, during a retreat, Amazon executives realized that they had the skills necessary to operate and execute scalable, effective data centers. The rest is history.
AWS is the world’s leading provider of cloud solutions, providing IT infrastructure solutions on an as-needed basis for companies of all sizes. Prominent companies that utilize AWS include Netflix, Expedia, Hulu, Spotify, and Ubisoft. AWS is a complex and highly customizable platform that works best for companies that run non-Windows services.
Difference Between AWS and Azure
Here are some points mentions the difference between AWS vs Azure
Documentation and simplicity of use
The AWS interface is feature-rich and simple to use, and the service comes with extensive, informative documentation. Azure organizes all of your account details and stores them in one place. However, its documentation is more challenging to understand and locate.
Licensing and license mobility
The licenses offered by AWS are more flexible and come with a greater variety of features. Microsoft Azure is more convenient for Windows administrators to set up and offers more SaaS options.
Networking and content delivery
Using AWS virtual private cloud, users may create secure, private networks in the Cloud (VPC). Azure uses a virtual network instead of a VPC. A VPN gateway that enables the communication between different networks.
Logging and monitoring
AWS SageMaker uses Cloud-Watch to record model metrics and data over time. For capturing and tracking data, Azure ML Studio uses ML-Flow.
Open-source development
AWS supports Linux and has connectors for open-source apps, and it is ideal for developers working on open-source software. Microsoft Azure is just now opening its doors to open-source developers.
Processes for deploying applications
AWS has services like Elastic Beanstalk, Batch, Lambda, and container services but only needs some to host apps. Azure has many ways to deploy apps, such as cloud services, container services, functions, batches, and app services.
Cloud market growth
Amazon made $13.5 billion in the first quarter of 2021, much more than the $10.33 billion it made in the first quarter of 2020. Azure's Q2 2021 revenue rose 50%, surpassing experts' predictions of 46% but falling short of last year's 59%.
Why Do We Fall? AWS and Cloud Domination
In the AWS vs Azure battle, AWS had an unprecedented upper hand. AWS was first launched in 2002 and its earliest competitor, Google, didn’t arrive until 2009. Microsoft didn’t step into the cloud market until 2010. Microsoft believed that the cloud infrastructure was just a trend that was soon going to fade away. However, after Amazon’s success, Microsoft had to play catch up.
When Azure first launched, it was not received well and faced many challenges, especially when compared to AWS. AWS had been running for almost 7 years and as a result, they had more capital, more infrastructure, and better and more scalable services than Azure did. More importantly, Amazon could add more servers to its cloud infrastructure and make better use of economies of scale—something that Azure was scrambling to do. This was a setback for Microsoft—not only was Microsoft dethroned as the leader in software infrastructure, but it was now being shown the door by a non-IT newbie.
Mind If I Cut In? Azure’s Redemption
The tide soon changed for Azure. Microsoft quickly revamped its cloud offering and added support to a variety of programming languages and operating systems. They made their systems more scalable and made peace with Linux. Today, Azure is one of the leading cloud providers in the world.
AWS vs Azure: Making the World a Better Place
Both Amazon and AWS technologies have, in their own way, contributed to the welfare of society.
For example, NASA has used the AWS platform to make its huge repository of pictures, videos, and audio files easily discoverable in one centralized location, giving people access to images of galaxies far away.
Similarly, People in Need, a nonprofit organization, uses AWS to scale an early warning system that alerts about 400,000 people in Cambodia when floods threaten. This technology has not only helped save hundreds of lives but has also made available a cost-effective method that can be replicated by other at-risk regions.
The Azure IoT Suite was used to create the Weka Smart Fridge, which keeps vaccinations properly stored. This has helped nonprofit medical agencies ensure that their vaccinations reach people who otherwise don’t have access to these facilities.
Azure is also used to find solutions to the world’s looming freshwater crisis. By working with Microsoft Azure, Nalco Water, the main water operational unit within Ecolab, uses cloud computing and advanced analytics to create solutions to help organizations reuse and recycle water.
Aggressive Expansions - AWS vs Azure: Which is Better?
Azure and AWS are both well-respected members of the cloud domain. They fight for a larger piece of the cloud pie and take the world by storm while doing so. Azure holds about 29.4% of all installed application workloads while AWS stands at 41.5 percent and Google holds just 3 percent of all installed application workloads.
In 2017, AWS’s market share featured at 47.1 percent with Q4 revenue of $3.66 billion, while Azure’s market share didn’t rise above 10 percent with a revenue of $6.9 billion (of course, Microsoft’s revenue figures are higher because their cloud division includes both Azure and Office 365).
However, in its recent Q1 FY 2018 earnings report, Microsoft's revenue from Azure grew over 90% this year, doubling the growth rate of AWS.
The Game Has Changed - The Cloud is the Future: Are You Ready?
Cloud computing allows companies to get new products on the market faster, increase efficiency, lower operational costs, improve interdepartmental collaboration, reduce capital expenditures, and increase innovation.
Companies that are ill-equipped to handle these changes could run the risk of falling behind.
However, to make the move to the cloud, organizations must have trained professionals on the job who are certified in cloud computing. Certified professionals can easily address the concerns that may arise during the transition to the cloud and are familiar with the nuances of cloud-based computing.
Due to this need for certified professionals, a huge demand for skilled employees has been largely unmet. LinkedIn reports that cloud and distributed computing topped the list of sought-after skills in both 2016 and 2017. Dice reports that job listings for the AWS cloud platform increased by 76 percent between 2015 and 2016. In 2015, 3.9 million jobs were affiliated with cloud computing Bootcamp in the United States and over 18 million worldwide. For qualified professionals, salaries are very high and competitive. According to Forbes, jobs in cloud computing are well compensated with an average salary of $125,591 for AWS certified professionals.
With the onset of cloud computing, several major cloud providers quickly rose to dominance but today, AWS and Azure lead the industry. These two cloud hosting platforms drive much of the job growth in the cloud computing space which leads to a dilemma for job seekers. With both AWS and Azure as dominant players in the market, which cloud certification makes the most sense for your career path? Should you pursue AWS certification or Azure certification? There are benefits and drawbacks to each certification which should be considered before choosing which one to pursue.
The Awakening - AWS vs Azure: The Certification Game
When it comes to the differences between AWS vs Azure, there are plenty. Both come with their own advantages and disadvantages. AWS and Azure are the two top players in the cloud technology space because both are very good at what they provide in different ways. In order to narrow down which platform is the right one to become certified in, an evaluation of the benefits of each certification is warranted.
The Benefits of AWS Certification: Although Azure is rapidly gaining market share, AWS is still by far the largest cloud computing service provider in the world today. AWS certification carries extra weight because of additional marketability due to the number of companies utilizing the platform. In addition, AWS certification grants access to the AWS Certified LinkedIn Community and other AWS certified professionals.
There are several AWS certifications for Developers and professionals to choose from, including AWS SysOps Associate, AWS Developer Associate, gcp certification, and Cloud Architect Certification.
The Benefits of Azure Certification: An Azure certification is backed by the Microsoft brand, giving the added benefit to candidates familiar with the in-house data platforms. Azure is used by over 55 percent of all Fortune 500 companies and gaining Azure certification increases the possibility of candidates finding a job in one of these companies. In addition, about 365,000 new companies adopt Azure every year, regularly increasing the need for Azure-certified professionals. Several Azure certifications are available to choose from, including Cloud Solution Architect, Developing Microsoft Azure Solutions, Architect Microsoft Azure, Implementing Microsoft Azure, and Cloud Architect.
Both AWS and Azure are considered to be adaptable, reliable, and resolute—much like the superheroes, we all admire. They help us solve global problems and make our lives easy. They adapt to the needs of their customers and lend a hand to governments and companies in solving various social and logistical issues. Sure, superheroes have helped their citizens and kept them safe, but cloud service providers like AWS and Azure have helped professionals revolutionize their industries without having to break the bank. Cloud systems have made it possible for companies like Uber, Salesforce, and Facebook to exist—all services we take for granted today.
Comparison of AWS vs. Azure
- Pricing - Azure and AWS cater service and pricing based on requirements. However, AWS is rated on an hourly basis and Azure on a minute basis. Azure offers higher flexibility in short-term subscriptions.
- Compute and computation services - With so much data being generated these days, there is always a demand for speedier processing methods. Compute services ensure that instances can be spawned in minutes and scaled up instantaneously if necessary. Both AWS and Azure deliver services to meet these requirements.
- Development tools - AWS includes two serverless tools, AWS Fargate and Lambda. Azure Function is a serverless platform that, when combined with Azure DevOps pipelines, allows you to streamline and manage complicated workflows. Azure Bot Service, Time Series Insights, IoT Edge, Stream Analytics, and more IoT and AI capabilities are available.
- Storage services - Long-lasting and reliable storage services are offered by both AWS and Azure. Moreover, Azure caters to storage services such as Blob Storage, Disk Storage, and Standard Archive, whereas AWS caters to services such as AWS S3, EBS, and Glacier.
- Database services - Nowadays, data is created in a variety of formats, therefore the databases that store data must remain updated. AWS and Azure offer different database services to manage both structured and unstructured data. Azure has Azure SQL Server Database, and AWS has Amazon RDS.
- Networking services - The Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) makes it possible to build private networks within the Cloud. Similar to VPC, Microsoft Azure Virtual Network enables you to do all of VPC's functions. Both clouds offer firewall options as well as options to expand the on-premise data center into the cloud.
- Container and Orchestration Support - AWS offers Big Data and analytics solutions that are more advanced. Depending on requirements, it can offer a wide range of services in the areas of IoT, mobile app development, or building a computing environment. They also provide Docker support. Microsoft competes in this space and may go a step further by providing Hadoop support through services such as Azure HDInsight.
- Compliance - Amazon has excellent relationships with government agencies, resulting in enhanced government cloud offerings. They also give excellent security features to ensure that individual users have proper access. Microsoft provides over 50 compatible products.
- Security Features - AWS caters a brilliant job of selecting secure alternatives and default settings to provide enhanced privacy. Azure relies on Microsoft's Cloud Defender service for security and data privacy, which is powered by artificial intelligence and safeguards against new and existing threats.
- Machine Learning - AWS and Azure both feature machine learning studios for developing machine learning models. Unlike Amazon SageMaker, Azure's studio does not necessitate a thorough understanding of data engineering, Python coding, and open-source libraries.
- Job Opportunities and Salary - AWS experts make an average of 6.3 lakhs per year, whereas Azure professionals earn approximately 6.1 lakhs per year. These being the two most common clouds, there is a plethora of job opportunities for AWS and Azure professionals.
- Market Share - Amazon reported revenue of $13.5 billion in the first quarter of 2021, exceeding analyst projections of $13.1 billion. When Amazon reveals AWS revenue, Microsoft discloses Azure growth rate. This resulted in a 50% increase in revenue over the preceding quarter in Q2 of 2021, exceeding the 46% growth projected by analysts.
- Establishment - AWS launched public in 2006, offering services such as Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) and Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3). Microsoft Azure, formerly known as Azure, was founded in 2010 to provide businesses with a reliable Cloud Computing platform. Azure was rebranded 'Microsoft Azure' in 2014, however, the term 'Azure' is still frequently used.
- Availability Zones - The supported regions and availability are the first things to consider when choosing a cloud space provider. Amazon Web Services is organized into 22 geographical areas and 14 data centers. Over 114 edge sites and 12 Regional Edge Caches are available. Microsoft Azure is divided into 54 regions, each of which has at least three availability zones and 116 edge locations.
Key Differences Between AWS and Azure
- Customers of AWS EC2 can configure their VMS or pre-configured images, whereas Azure users must select a virtual hard disc to construct a VM that has been pre-configured by a third party.
- AWS provides temporary storage that is assigned when an instance is launched and destroyed when it is terminated. In contrast, Azure provides temporary storage via block storage with page Blobs for VMs and Block Blobs for object storage.
- Azure accepts hybrid cloud systems, however, AWS does not accept private or third-party cloud providers.
Advantages and Disadvantages of AWS
Advantages
1. Innovation: AWS's innovative features can benefit your cloud operations. It also aids in assessing your company's current status, planning for the future, and solving any issues that may have arisen.
2. Easy to use - AWS is user-friendly. The platform's design is optimized for user efficiency. AWS Management Console lets you quickly access inbuilt apps and services or add a SAAS app. The system can be used without coding or technical knowledge. Companies hire AWS-certified IT professionals for smooth operations.
3. Cost-effective - Small businesses like AWS because of its affordability. No upfront payment is required. The versatile technology lets users extend space to meet corporate needs. Launching a product is difficult. AWS clients can start with a basic package and upgrade as needed.
Disadvantages
1. Limitations on security: The availability of AWS resources varies by area. The controls for Amazon EC2 and Amazon VPC administer these limits. This is done to prevent users from squandering resources and unnecessary costs. In addition, it serves as a preventative step, making it less likely that those with ill intentions will use its facilities to carry out attacks.
2. Cloud computing issues - Although Cloud Computing has caused a stir in the IT sector, it has its share of issues. Millions of users could experience disruptions in service owing to power outages or network problems. Backup security, data leakage, and user privacy have all been mentioned as points of contention.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Azure
Advantages
1. Improved scalability -With Azure, you can build apps that function smoothly, without interruption, and expand from 10 to ten million clients without further coding. The cloud storage services offered by Azure are robust, secure, and efficient in terms of both performance and cost. Adding more processors to the application and adjusting its settings is without hassle.
2. Business sustainability - Businesses prefer Azure because of its rapid reaction time and short development cycles, encouraging curiosity about the platform's lesser-known capabilities.
3. Higher availability and redundancy - There are three hallmarks of Azure's service offerings. Access to its cloud services is simple, safe, and expandable, and it gives all three. As a storage system, it is unparalleled in both speed and efficiency.
4. Hybrid capabilities - Azure offers hybrid capabilities that make it unique. Azure offers seamless mobility and a stable uniform platform across on-premise and public clouds. Azure offers hybrid connections to boost usability and speed, including VPNs, caches, CDNs, and Express-Route.
5. Security and disaster recovery - No other cloud service can compare to Azure regarding data security. Azure SQL databases and virtual machines may be backed up with only a click. Microsoft Azure's data recovery time is 66% faster than an on-premise IT solution in service interruption or data loss.
Disadvantages
1. Requires management - You'll still require data management even though you'll save on IT hardware and upkeep locally. Microsoft Azure doesn't manage cloud data centers. It means you'll require ground staff that knows about using Azure, which involves server management and upgrading. It would be best if you learned that talent or found another way.
2. Requires expertise - Business computing power is one of Azure's main challenges. Moving from being on systems to the Cloud may mean losing processing power. This cloud-based platform may cost several thousand dollars annually to generate the same computing power.
Rise or Fall?
The article has explained, the pros and cons, and the differences between AWS vs Azure. So who’s to say what will come next? In 2015, no one thought Azure could catch up; but they’ve proven the naysayers wrong. The cloud wars are unpredictable and exciting. Who would you count on - AWS or Azure? Will Azure overtake AWS? Will Google Cloud be the underdog that will disrupt the cloud domain? Only time will tell. But one thing is certain - the battle between AWS vs Azure may continue, but the cloud is here to stay.
In the ongoing debate between AWS and Azure, the AWS Solution Architect Certification stands out as an important player in the professional world. While both AWS and Azure provide a diverse set of cloud computing services and capabilities, AWS is frequently praised for its extensive service offerings, robust global infrastructure, and pioneering role in the cloud industry.
A Note from the Illustrator
I love "Raiders of the Lost Ark" like many people out there and so we structured the story based on it. The way the heroes in the comicographic take punches, that's Indy. The comicographic does not have a definite conclusion and curiosity is maintained with the rat at the end, that's all Raiders! The film's soundtrack was the real power-booster for me while I illustrated the comicographic for 2 months, I even dreamt about the music after I was done working on it! It is the finest popcorn movie ever made, the only reason it's not the greatest blockbuster film ever made is that it wasn't the 1975 movie with a certain Shark named Bruce dying in the end.
It's a real thrill paying homage to some of my favorite comic book artists through the comicographic like--Jack Kirby, Alex Ross, Jim Lee, Frank Cho, and many more. - Chetan Ramesh
Become an AWS Wizard with our in-depth Cloud Architect Master’s Program. Enroll now!
FAQs
1. Why is AWS popular than Azure?
Microsoft Azure and AWS both offer comparable services, but both are trying to take the top spot. It is clear from the AWS vs. Azure comparison that AWS is more well-known than Azure, yet the market share and revenue growth figures show that Microsoft Azure entered the market more quickly.
Due to its almost 7-year operating history, AWS has greater resources, infrastructure, and superior, scalable services than Azure. More significantly, while Azure was attempting to catch up, Amazon could expand its cloud infrastructure by adding more servers and utilizing economies of scale more effectively.
2. What is the difference between Azure and AWS?
Azure is regarded as a Platform as a Service (PaaS) as well as an Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provider. Because of its parent business, Azure is a very potent offering. Microsoft offers an infrastructure support level that is comparable to a few other businesses. On the other hand, AWS has a big toolkit that is expanding exponentially, much like Amazon itself. AWS has more than 10 years of experience in the cloud computing sector, making it the market leader and has been for some time. Platform as a Service (PaaS), Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), and Software as a Service are the three categories under which AWS services fall (Saas).
Google Cloud vs. AWS: Choosing the Right Platform
Table of Contents
As cloud computing continues to find its way into many big and small organizations, the choice of the right cloud computing solution has become a talking point for specialists and business owners alike. Among public cloud providers, Amazon Web Services (AWS) seems to have the lead in the competition, with Google Cloud and Microsoft Azure close behind.
In this article, we compare the two leading cloud computing services – Amazon Web Services’ Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) and Google Cloud’s Google Compute Engine (GCE) – on the basis of their performance, cost, features, services, and the overall advantages and disadvantages of these two cloud computing platforms. Beyond helping you choose the right Internet as a Service (IaaS) platform, we hope this comparison also helps the eager professionals among you understand where you would have to focus your learning efforts.
As cloud computing continues to find its way into many big and small organizations, the choice of the right cloud computing solution has become a talking point for specialists and business owners alike. Among public cloud providers, Amazon Web Services (AWS) seems to have the lead in the competition, with Google Cloud and Microsoft Azure close behind.
In this article, we compare the two leading cloud computing services – Amazon Web Services’ Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) and Google Cloud’s Google Compute Engine (GCE) – on the basis of their performance, cost, features, services, and the overall advantages and disadvantages of these two cloud computing platforms. Beyond helping you choose the right Internet as a Service (IaaS) platform, we hope this comparison also helps the eager professionals among you understand where you would have to focus your learning efforts.
Build and Deploy Azure Applications Like a Pro!
Some Striking Contrasts Between EC2 & GCE
AWS has been the cloud computing market-leader for the past seven years. Available in more zones and regions than Google Cloud, licensed users are assured of minimal impact of outages. In addition, AWS boasts a wide array of services, many of which -such as the Simple Email Service and the CloudFront content delivery network- are not available in GCE.
AWS also offers micro-Windows instances as part of its Free Usage Tier, whereas support for Windows workloads is not a part of GCE’s offerings. As Jillian Mirandi, a tech analyst points out, “AWS has a more complete, enterprise-grade portfolio”.
AWS also customizes its networking equipment, the corresponding protocols that travel over it to boost network performance, and also has its own fiber-optic network between zones. Google’s edge in network performance is not perceived to last long.
Now for some noteworthy advancements made by Google Cloud’s GCE.
GCE’s impressive network performance is something to note. It is largely because Google’s network traffic passes through its own fiber network rather than traversing the public internet. Each GCE instance is also attached to a single network that spans all regions without VPNs or gateways as middlemen.
On the whole, considering the number of services available, AWS is in a league of its own, well ahead of GCE. The varied services AWS offers are well-integrated and provide a very comprehensive cloud solution. AWS, it is proclaimed, has no rivals with regard to platform completeness and the productivity level that you can reach.
However, the choice of the right platform does depend upon the needs of the enterprise.
AWS has been the cloud computing market-leader for the past seven years. Available in more zones and regions than Google Cloud, licensed users are assured of minimal impact of outages. In addition, AWS boasts a wide array of services, many of which -such as the Simple Email Service and the CloudFront content delivery network- are not available in GCE.
AWS also offers micro-Windows instances as part of its Free Usage Tier, whereas support for Windows workloads is not a part of GCE’s offerings. As Jillian Mirandi, a tech analyst points out, “AWS has a more complete, enterprise-grade portfolio”.
AWS also customizes its networking equipment, the corresponding protocols that travel over it to boost network performance, and also has its own fiber-optic network between zones. Google’s edge in network performance is not perceived to last long.
Now for some noteworthy advancements made by Google Cloud’s GCE.
GCE’s impressive network performance is something to note. It is largely because Google’s network traffic passes through its own fiber network rather than traversing the public internet. Each GCE instance is also attached to a single network that spans all regions without VPNs or gateways as middlemen.
On the whole, considering the number of services available, AWS is in a league of its own, well ahead of GCE. The varied services AWS offers are well-integrated and provide a very comprehensive cloud solution. AWS, it is proclaimed, has no rivals with regard to platform completeness and the productivity level that you can reach.
However, the choice of the right platform does depend upon the needs of the enterprise.
How to Become a Cloud Engineer? A Complete Guide
By now, it is quite clear that cloud computing is changing the way businesses function, creating a new paradigm of choice to deliver and manage data and applications. Today, you can see that many companies have invested in and shifted to cloud computing for various reasons.
A report by IDC predicts that global spending on public cloud infrastructure and related services will reach around $500 billion by 2023—up from $229 billion in 2019. And, as is the case with any technology that’s growing that fast, so are related job opportunities.
In this article, we will discuss how you can become a cloud engineer. Before learning how to become one, however, you must first understand the fundamentals of cloud computing, and why you should think about becoming one.
What is Cloud Engineering?
Cloud engineering encompasses devising, managing and maintaining resources of computer infrastructure. With growing technology, the importance of Cloud engineering is gaining momentum. Cloud technology has enabled you to stream your favorite shows online and listen to songs with unlimited access. It uses engineering principles to design systems, and everybody wants to know how to be a cloud engineer.
Cloud engineers solve the computing problems of an entity or consumers. The services provided are software as a service (SaaS), platform as a service (PaaS) and infrastructure as a service (IaaS). As a cloud engineer, you will be in charge of storing, managing data and proceeding with timely software updates. In totality, you will supervise the cloud system running smoothly without any obstacles.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing refers to services like storage, databases, software, and analytics that are made accessible via the internet. According to Gartner, the cloud tech services market is expected to grow from $175.8 billion in 2018 to $206 billion in 2019—a rise of 17.3 percent in a single year.
As of 2020, it is expected that 90 percent of all organizations in the world will be using cloud services in some form. Today, various companies and organizations claim that cloud computing services have helped their employees perform better and experiment more, especially in fields like machine learning and artificial intelligence.
What Does a Cloud Engineer Do?
A Cloud Engineer, proficient in technology, is responsible for designing, implementing, and managing cloud infrastructure and services. They overlook the technical workload associated with cloud computing and focus on building and sustaining the cloud-based framework. As a Cloud Engineer, your role involves identifying and integrating private and public cloud computing services to ensure secure and error-free operations for the organization. Additionally, you will deploy applications, monitor performance, and optimize cloud environments. Collaborating with cross-functional teams, you will troubleshoot issues, implement best practices for cloud security and cost optimization, and stay updated with the latest advancements in cloud technologies. Continuous improvement of cloud infrastructure to meet organizational needs is also part of your responsibilities.
Below mentioned are some of the day-to-day cloud engineers.
- Transferring an organization’s computer system data or infrastructure to their cloud systems.
- Systematizing cloud infrastructure elements like networking and security services
- Creation of applications and databases that function on the cloud.
- Monitor the cloud management and data storage services.
- Assuring the safety and security of the data.
- Registering, overseeing and providing client services in case of cloud-based issues.
What Are the Career Paths of a Cloud Computing Engineer?
A cloud engineer is an IT professional responsible for all the technical aspects of cloud computing like planning and design, maintenance, and support. A cloud computing engineer can take up several different career paths, including:
- Cloud developer
- Front-end/back-end developer
- Solutions architect
- Cloud architect
- Data engineer
- Security engineer
- Development operations engineer
- Full-Stack developer
- SysOps administrator
Major Cloud Computing Roles
Solutions Architect
Solutions Architects are responsible for analyzing the technical environment, requirements, specifications. These professionals are required to select appropriate technologies that meet business needs. They estimate and manage usage and operational costs of the solutions they provide and support project management, development, and operations teams.
SysOps Administrators
SysOps Administrators deploy, manage, and operate highly scalable and fault-tolerant cloud-based and hybrid systems. These professionals select an appropriate service based on computing, security, or data requirements. They estimate and manage infrastructure and services usage and operational costs. They are also experts on how to migrate on-premises workloads to the cloud.
Skills and Qualifications
Here are the steps you must undertake to become a cloud engineer:
Complete your bachelor’s
A bachelor’s degree in Computer Science or a related field is required to become a cloud engineer. Cautiously choose a bachelor's program that concentrates on the technical perspective of software, computing and system framework. For further specialization, you can pursue a master’s degree for a bevy of opportunities.
Expertise in Programming Languages
Learning programming languages is a must to become a cloud engineer. Java, Python, Ruby, and so on are essential languages to add to your portfolio. Get acquainted with cloud services like Azure, AWS, GCP, Oracle and Hadoop.
Learn skills
Familiarize yourself with cloud security, machine learning, and cloud deployment. Advanced certifications. Additional technical knowledge always goes a long way. A combination of program management, Network+, Security+ and other certifications help the portfolio.
Hard Skills
- A deep understanding of operating systems like Linux, Ubuntu and Windows is required.
- Clarity in networking concepts is crucial for the development of a secure and scalable computing system.
- A cloud engineer must be aware of terms like Hypertext transfer protocol secure (HTTPS), Virtual private network (VPN), Internet Protocol (IP), Domain name system (DNS) and others.
- Devising an unassailable network and having knowledge of numerous security protocols is vital.
- Cognition of open standards is required for tagging, driving and describing the data.
Soft Skills
- Cloud engineers should be excellent in communication as they frequently collaborate with IT professionals.
- Remarkable leadership skills are important since you might handle a team of tech professionals. As a leader, identifying a team's strengths and weaknesses helps produce distinctive outputs.
- Having a keen eye for detail is appreciated in a cloud architect. From design to troubleshooting, everything falls in your arena. So, being vigilant is important.
- A relentless drive and hunger to learn new things and experiment will make you stand out from the rest.
Types of Cloud Engineering Roles and Responsibilities
Let’s dive deeper into the job descriptions of each of them.
Cloud Developer
As the name suggests, a cloud developer is responsible for coding and devising applications. They must possess knowledge of Cloud architecture. From the development of applications to the deploying and debugging of cloud-based apps, cloud developers must know it all. They write. Correct and debug code modules.
System operating Engineers
SysOps Engineers compute potential issues that are likely to arise in the functioning of applications. They contemplate a backup strategy for unpredictable circumstances and have accurate access controls for maintaining the probity of the organization's data. They act as the system administrators after the development of the application. They must have prior background in monitoring and auditing systems.
How to Become a Cloud Engineer: Steps to Enter the Field
Step 1: Earn a Bachelor’s Degree
Having a formal education is extremely important in a technical field. If you would like to become a Cloud Engineer, then attaining a Bachelor’s Degree in computer science or related field is definitely your first step. In addition to looking great on a resume, they also offer a broad scope on the theory of the subject. They can also be a criteria by most companies for hiring. Most Cloud Engineers graduate with a cloud computing certification/engineering.
Step 2: Gain Proficiency in a Cloud Computing Platform
The first and foremost step to becoming a cloud engineer is to be proficient in at least one of the three major cloud computing platforms—AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud Platform (GCP). There are many resources that you can find on the internet, like YouTube videos, educational articles, and virtual or physical training, to gain a basic understanding. Once you’ve done that, you can move on to can get certified in any of the respective environments.
For AWS, various certifications can be divided into four categories:
- Foundation (basic)
- Associate
- Professional
- Specialty-level
Similarly, for Azure, there are multiple training paths and certifications, as the graphic below indicates:
Most cloud computing platforms also offer a free tier of service. This is especially useful while you are choosing which provider to move to—or, whether you want to migrate your workloads to more than one cloud-based on your business requirements and the ROI you want to achieve.
Step 3: Having Experience in at Least One Programming Language
Unlike general-purpose programming languages like C and C++, cloud computing requires more data-oriented programming languages, such as Python, Java, and Clojure. To learn these, you can use blogs, videos, online/offline classes, and other free resources.
Step 4: Earn Relevant Certifications
Having professional certifications are a must for cloud engineers to help showcase their knowledge and skills. Popular certifications include:
- AWS certifications - Cloud Practitioner, Solutions Architect, Developer, SAP on AWS, and SysOps Administrator.
- Google Cloud Platform certifications - Professional Cloud Architect, Professional Cloud Developer, and Professional Cloud Security Engineer
- Microsoft certifications - Microsoft Certified: Azure Developer Associate and Microsoft Certified: Azure Fundamentals
Step 5: Specializing
Apart from gaining knowledge in cloud computing platforms and being experienced in at least one programming language, you will also need some understanding of key concepts like:
Storage and Networking
With storage, you need to know the different ways you can store data and where you can access it from. It is also vital that you have some experience with the services Azure and AWS provide, like AWS S3 and Azure Storage in Microsoft Azure. You also need to have a strong understanding of the fundamental concepts of networking.Virtualization and Operating Systems
While you are leveraging physical infrastructure in cloud data centers, most of what you will be configuring and managing are virtual machines (VMs) that run on the hardware. You also need to understand how those VMs work on virtual networks in the cloud. Public clouds are also OS-agnostic, so you should have a good grasp of Windows and Linux operating systems.Security and Disaster Recovery
Data, applications, and infrastructure must be protected from cybersecurity threats and malicious attacks. You should be prepared for any unexpected circumstances by making sure that your systems are safe and regularly backed up to circumvent any data loss.Web Services and DevOps
Do you have a strong understanding of how cloud computing can provide a centralized platform, on which you can perform testing, deployment, and production for DevOps automation? Moreover, with DevOps, do you understand the synergy needed between the operations and the development teams? In today’s agile, dynamic world, this is a must.
Step 6: Internships
Internships are a great way to gain experience in the cloud industry. They are also a great way to get your foot in through the door and also provides you with a hands-on approach to what the actual job will entail. You can start applying for internships while studying or for choosing your specialization.
After working in the field of IT for over 30 years, Jerry Stark was laid off during the 2020 pandemic. He then enrolled in the Cloud Architect Masters Program and was able to land a job soon after the course. Read about his success story in our Simplilearn Cloud Architect Review here.
Why Learn Cloud Computing?
The importance of tech and cloud computing is no longer unknown to the world. The cloud is constantly changing the way people perceive and consume things. Everything is now based on the cloud, from streaming unlimited shows to running a business. With growing necessity, the demand for professionals who will handle the cloud is skyrocketing. There is a whopping boost in the number of cloud engineers. It reduces operation costs and negates the probability of human error. It is reinventing the medium of entertainment, knowledge and work.
Career Outlook
Recent studies at The Bureau Of Labour Statistics show a whopping demand hike for Cloud Computing engineers. Between the years 2020 to 2029, it is expected to rise by at least 5 per cent. The arena of opportunities is high in the cloud computing sector which makes me all the more in demand. Below mentioned are a few roles
- Front-end/Back-end developer
- Data Engineer
- Cloud Developer
- Security Engineer
- Solutions Architect
Cloud Engineer Salary
Cloud computing engineers fetch high salaries, too. According to Payscale, in the United States, they earn an average of around $116,800 annually, and in India, a cloud computing engineer is paid approximately ₹ 6,66,800 per year. In fact, the more experience you gain in cloud computing, the better chance you will have of earning a higher salary.
Who Can Become a Cloud Engineer?
With the right amount of qualification and hands-on practical and technical experience, anyone can become a cloud computing engineer. Thorough knowledge and familiarity with tech terms are essential. As the experience grows, you become proficient and advanced. Narrowing down your specialization can help you further in the long run.
Benefits of Being a Cloud Engineer
Secure Career
Cloud computing is for the long run, and the world knows it. Not only is it the backbone of many IT organizations, but also essential for day-to-day work. With cloud computing accessing data has become so easy. Hence, it will only boom shortly. Cloud computing is reaching new heights each day without giving any indications of its downfall. According to the World Economic Forum, more than half of the children in primary school will have a career that does not exist today.
Respectable Profession
Besides being the most in-demand, Cloud architect is also one of the most highly regarded professions. It is revolutionizing the face of IT and you will be the martial to lead the generation into the new light.
Constant Motion
In Cloud Computing, you will be witnessing new inventions and modulations on a day to day basis. You will be moving forward and will not be stagnant. The specialization of skills will always keep you in demand and never go out of fashion,
Handsome Pay
IT companies are spending an unimaginable amount on Cloud computing. The average salary of a cloud architect in India is approximately 9 lakhs to 11 lakhs. It will automatically put you above half of the population.
Choose The Right Cloud Computing Program
This table compares various cloud computing programs offered by Simplilearn, based on several key features and details. The table provides an overview of the cloud computing courses' duration, skills you will learn, additional benefits, among other important factors, to help you make an informed decision about which course best suits your needs.
Program Name AWS Solutions Architect Cloud Architect Masters Program Caltech Cloud Computing Bootcamp Geo All All US University Simplilearn Simplilearn Caltech Course Duration Self Paced 11 Months 6 Months Coding Experience Required Basic Knowledge Basic Knowledge Basic Knowledge Skills You Will Learn 10+ Skills Including AWS Solution Planning, AWS Cost Estimation, AWS Data IO, etc. 30+ Skills Including EC2, ECS, Lambda, CloudFormation, ELB, etc. 10+ Skills Including Application Migration, Autoscaling, MultiCloud Deployment, etc. Additional Benefits 16+ Live Demos of AWS Services
Real-Time Industry Projects
Simulation ExamsMasters Certificate
Capstone Projects
Exam Voucher IncludedCaltech's Academic Excellence
Live Classes by Experts
Career Services








Comments
Post a Comment